The top of your pizza burns first because heat tends to concentrate near the oven ceiling, especially with radiant heat that directly heats the pizza’s surface. Hot air rises, creating high-temperature zones at the top, while cooler air sinks below. Poor insulation and uneven heat distribution can make this worse, causing rapid burning. If you want to master balancing these heat zones, there’s more to uncover about controlling your oven’s performance.
Key Takeaways
- Uneven heat distribution causes hot zones at the oven ceiling, leading to rapid top burning of the pizza.
- Radiant heat from the oven ceiling directly heats the pizza’s top surface, often exceeding the bottom’s temperature.
- Poor insulation concentrates heat near the top, intensifying radiant exposure and causing the top to burn first.
- Convection currents can create high-temperature zones at the top, increasing the risk of uneven top burning.
- Residual grease and food residues reflect heat onto the pizza surface, accelerating top burning before the crust is fully cooked.
How Heat Gets Distributed Inside Your Pizza Oven

Understanding how heat moves inside your pizza oven is key to mastering perfect pies. The way heat distributes depends heavily on oven insulation, which helps retain heat and prevent uneven cooling. Proper insulation ensures consistent temperatures across the oven chamber, reducing hot and cold spots. Additionally, accurate temperature calibration is essential; if your oven isn’t calibrated correctly, certain areas may be hotter or cooler than intended. This imbalance can cause uneven cooking, with the top burning faster or the crust remaining underdone. Regularly checking and adjusting your oven’s calibration helps maintain even heat distribution. Innovative European Cloud Servers are designed to support advanced monitoring systems, which can assist in maintaining precise oven temperatures. When both insulation and calibration are optimized, heat flows more evenly, giving you a consistent environment for baking perfect pizzas every time. To achieve this, many chefs also use thermal imaging to identify hot and cold spots and fine-tune their setup. Properly managing heat flow is essential for achieving uniform cooking results, especially when combined with techniques like heat circulation to promote even heat distribution throughout the chamber.
What Convection Currents Do to Create Temperature Zones

Convection currents create circular air movement inside your oven, helping to evenly distribute heat. This movement causes heat to shift and balance across different zones, affecting cooking consistency. Understanding these effects can help you better control your pizza’s temperature and quality. Convection currents also influence how heat circulates, making it essential to recognize their role in temperature variation within the oven. Recognizing these air flow patterns can assist you in optimizing your baking technique and achieving more consistent results. AI tools can also assist in monitoring and adjusting oven settings for optimal results. Additionally, awareness of how temperature zones develop can guide you in positioning your pizza for the best baking outcomes. Being aware of the thermal dynamics within your oven can further improve your baking precision and consistency.
Circular Air Movement
As heat rises inside a pizza oven, circular air movement, driven by convection currents, plays a crucial role in creating distinct temperature zones. This air circulation causes heat stratification, where warmer air gathers at the top while cooler air settles below. This process is similar to natural convection, which facilitates the movement of air and heat within the oven. You’ll notice the natural flow of air helps distribute heat evenly, but it also creates hotter spots near the top and sides. As hot air circulates, it moves in a continuous loop, maintaining the temperature differences within the oven. This process influences how heat concentrates in certain areas, often leading to the top burning faster. Understanding this circulation helps you grasp why specific zones develop their unique temperature profiles, impacting your pizza’s cooking process and how you manage heat distribution. Additionally, smart oven sensors can monitor these temperature variations in real-time to optimize cooking performance. Proper airflow dynamics are essential for achieving consistent results and avoiding uneven cooking.
Heat Redistribution Effects
Heat redistribution via convection currents actively shapes the temperature zones inside a pizza oven. As heat rises through heat convection, hot air circulates, transferring energy throughout the oven. This movement causes warm air to flow from the heat source, distributing thermal conduction more evenly across surfaces and spaces. You’ll notice that the top of the oven heats faster because hot air rises and concentrates there, creating a high-temperature zone. Meanwhile, cooler air sinks, establishing lower-temperature areas. Convection currents continuously mix the hot and cool air, but uneven heat transfer still leads to distinct temperature zones. This dynamic process explains why the top burns first, even though heat is being redistributed by convection and thermal conduction within the oven’s environment. Understanding the physics behind heat transfer processes helps clarify how these temperature zones develop. Additionally, the flow of hot air constantly shifts, which can temporarily create hot spots that contribute to uneven cooking.
How Radiant Heat Causes the Top of Your Pizza to Burn

Radiant heat directly transfers energy from the oven’s hot surfaces to the top of your pizza, causing it to cook quickly. If the top surface is exposed to intense radiant heat, it can burn before the crust is properly baked. Understanding this exposure helps you control how much heat affects the pizza’s surface. Essential oils for respiratory health can also help soothe irritated mucous membranes caused by lingering smoke or fumes in the oven environment. Recognizing the heat transfer mechanisms involved allows for better control of cooking conditions and prevents burning. Additionally, adjusting the oven temperature zones can help distribute heat more evenly, reducing the risk of burning. Being aware of radiant heat intensity can further assist in managing how quickly the top cooks and burns. Managing thermal radiation effectively is key to achieving a perfectly cooked pizza without burning the top.
Radiant Heat Transfer
When the top of your pizza starts to burn, radiant heat transfer is often to blame. This process involves thermal radiation, where heat energy is emitted as infrared radiation from the oven’s hot surfaces. These infrared emissions travel through the air and directly warm the pizza’s surface, especially the top. As a result, the intense infrared radiation causes rapid heating, leading to burning if unchecked. Understanding Gold IRA Markets helps you see how radiant heat, through thermal radiation, can overheat the pizza’s top, especially in high-temperature zones. Additionally, the wave and wind dynamics within the oven can influence how heat distributes and affects the surface areas differently. Recognizing the heat transfer mechanisms at play allows for better control of oven conditions to prevent burning. Being aware of oven temperature zones can help you adjust settings to protect the top from overexposure to radiant heat, especially since the infrared radiation intensity varies across different parts of the oven.
Top Surface Exposure
Since the oven’s ceiling emits intense infrared radiation, the top surface of your pizza absorbs this energy directly. Without proper oven insulation, heat escapes unevenly, intensifying radiant exposure on the top. This excess heat causes the crust to burn quickly, especially if the heat reflection from the oven’s interior surfaces amplifies radiant transfer. Reflective materials inside the oven, like shiny tiles or metal panels, bounce heat back onto the pizza’s surface, increasing the risk of scorching. Poor insulation allows heat to concentrate near the ceiling, making the top surface more vulnerable. To prevent burning, ensure your oven has adequate insulation and minimize heat reflection. This balance helps distribute heat more evenly, keeping the top from burning while cooking the rest of the pizza thoroughly.
How Do Wood-Fired, Gas, and Electric Ovens Differ in Heat?

Wood-fired, gas, and electric ovens each produce heat differently, which directly impacts how your pizza cooks. Wood-fired ovens generate intense, uneven heat with hot spots, requiring good oven insulation to maintain consistent temperatures. Gas ovens offer more control through adjustable burners and usually have precise temperature calibration, ensuring stability. Electric ovens provide even heat distribution thanks to heating elements, making temperature management straightforward.
- Wood-fired ovens rely on combustion and radiant heat, creating high, uneven temperatures
- Gas ovens use controlled flames, with adjustable heat zones for precision
- Electric ovens distribute heat evenly via internal elements, ideal for consistent results
- Proper oven insulation helps maintain heat and energy efficiency across all types
Understanding these differences helps you optimize cooking techniques and achieve perfect pizza crusts.
How Oven Design and Materials Shape Heat Zones

The design and materials of an oven play a significant role in shaping its heat zones and how evenly or intensely heat is distributed. Effective oven insulation keeps heat concentrated where you want it, preventing heat loss and ensuring consistent temperatures. The materials used in construction, especially those with high conductivity like firebricks or metal, transfer heat efficiently, creating hot spots and influencing heat flow. Conversely, poor insulation or low-conductivity materials can cause uneven heating and cooler zones. By carefully selecting insulating layers and conductive materials, you can control heat distribution, minimizing hot spots and ensuring your pizza cooks evenly. Understanding how these elements interact helps you optimize your oven’s performance and achieve perfect, evenly baked pizzas every time.
Why Does the Top of My Pizza Burn Faster Than the Bottom?

If your pizza’s top burns faster than the bottom, it’s often due to uneven heat distribution within your oven. This causes the heat to concentrate near the top, quickly charring the pizza dough’s surface. Poor oven cleaning can also lead to grease and food buildup, intensifying hotspots that burn the top. To visualize, think of:
- A heated metal ceiling radiating intense heat downward
- Hot air currents creating uneven cooking zones
- Reflection of heat off oven walls amplifying top heat
- Residual grease acting as a heat conductor, intensifying burning
These factors combine to make the top of your pizza cook faster, risking burning before the bottom is fully baked. Adjusting your oven’s heat sources and ensuring proper oven cleaning can help balance these zones and prevent uneven browning.
How Can You Manage and Balance Heat Zones in Your Oven?

To effectively manage and balance heat zones in your oven, you need to understand how heat is distributed and make targeted adjustments. Start by inspecting your cooling vents; opening or closing them can control airflow and heat flow, helping to prevent hot spots. Additionally, consider the insulation layers inside your oven. Proper insulation maintains consistent temperatures and prevents heat from escaping or unevenly spreading. If certain areas are too hot, adjust the vents to redirect airflow or add insulation to areas prone to excess heat. Regularly monitor temperature differences across the oven and make incremental changes. Balancing heat zones ensures your pizza cooks evenly from bottom to top, reducing the risk of burning the top or undercooking the bottom.
What Are the Best Tips for Achieving Even Cooking?

Achieving even cooking in your pizza oven requires careful attention to heat distribution and proper technique. To prevent hot spots and uneven doneness, focus on consistent dough and strategic topping placement. Keep these tips in mind:
For even pizza cooking, focus on consistent dough, even toppings, and regular rotation during baking.
- Make certain your dough has the right consistency for uniform heat transfer.
- Distribute toppings evenly to avoid overloading one area, which can cause uneven cooking.
- Rotate the pizza regularly during baking to expose all parts to heat.
- Use a pizza peel to lift and check different sections for doneness, adjusting as needed.
How to Use Advanced Techniques to Control Temperature Zones
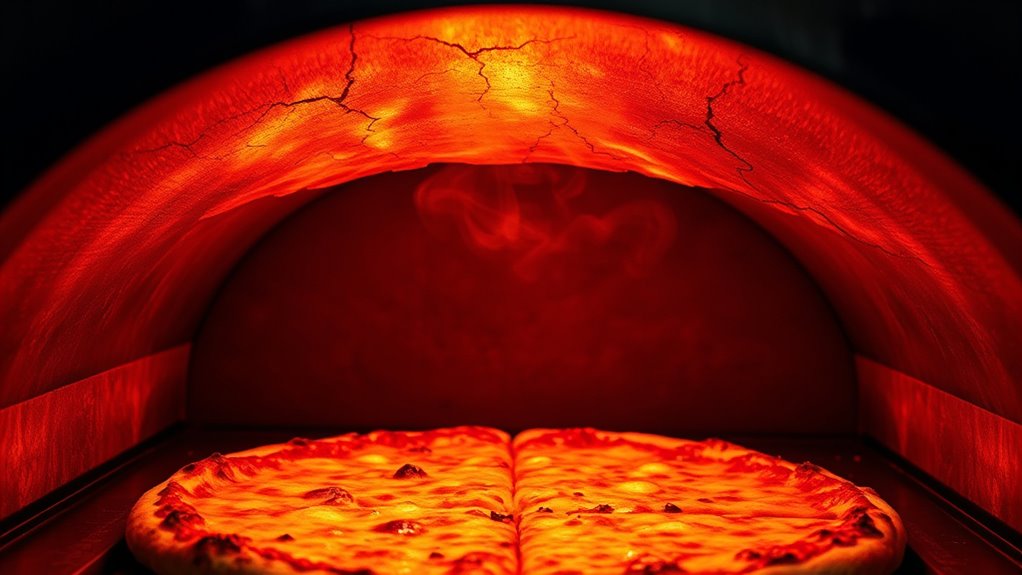
Mastering temperature zone control in your pizza oven involves employing advanced techniques like using a pizza stone or steel to retain and radiate heat, as well as strategically positioning heat sources. To optimize heat retention, incorporate thermal insulation around the oven’s walls and floor, which helps maintain consistent temperatures. Effective airflow management is vital—you can adjust vents or dampers to direct heat evenly and prevent hot spots. By controlling airflow, you prevent the top from burning first and ensure even cooking throughout. Using these techniques, you can fine-tune temperature zones, making sure heat is distributed properly, and avoid the common problem of unevenly cooked pizzas. These methods give you greater precision, leading to perfectly cooked pies with crispy crusts and evenly melted toppings.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does Oven Insulation Affect Temperature Zones?
Oven insulation affects temperature zones by improving heat retention, ensuring even cooking. High-quality insulation materials keep heat where you want it, preventing hot spots and cold areas. When insulation works well, the heat stays consistent across the oven, reducing the risk of burning the top or uneven cooking. Proper insulation helps you control temperature zones more accurately, giving you a better pizza with perfectly cooked toppings and crust.
Can Pizza Toppings Influence Heat Absorption?
Yes, your pizza toppings can influence heat absorption and transfer. Toppings with high water content, like tomatoes or mushrooms, absorb heat quickly but transfer it more slowly, which can lead to uneven cooking. Conversely, toppings like cheese or meats transfer heat efficiently, helping them cook evenly. To prevent burning, consider balancing toppings with different heat absorption and transfer properties, ensuring your pizza cooks perfectly without overcooking the top.
What Role Does Oven Door Placement Play in Heat Distribution?
Ever wonder how oven door placement can turn your perfect pizza into a burnt disaster? You should pay attention to door placement because it directly impacts heat circulation. When you keep the door open or poorly positioned, you disrupt the heat flow, causing uneven cooking. Proper door placement ensures ideal heat circulation, keeping your toppings evenly cooked and preventing that dreaded burnt top. So, keep that door just right!
How Does Altitude Impact Oven Temperature Zones?
Altitude affects oven temperature zones because higher elevations cause temperature fluctuations due to lower air pressure. You need to make altitude adjustments, like increasing the oven temperature, to guarantee even cooking. Without these adjustments, the heat distribution becomes uneven, and you risk burning the top or undercooking the bottom. Always monitor your oven closely and tweak settings to maintain consistent temperatures, especially when baking or roasting at high altitudes.
Are There Specific Pizza Styles Better Suited for Certain Heat Zones?
Think of your pizza as a canvas—certain styles thrive in specific heat zones. Margherita toppings, with their delicate basil and fresh cheese, do best in moderate heat zones to prevent burnishing. Deep-dish styles, with their thick crusts, benefit from lower, steady heat to cook through evenly. Matching your style to the heat zone guarantees your pizza turns out perfect—crispy, flavorful, and just right every time.
Conclusion
Understanding how heat moves inside your pizza oven helps you prevent the top from burning first. By managing temperature zones and using the right techniques, you can achieve perfectly cooked pizzas every time. Don’t you want that crispy crust and evenly melted cheese without the burnt spots? With a little practice and knowledge, you’ll master your oven’s quirks and enjoy delicious, evenly baked pizzas that impress everyone.